Accounting and Bookkeeping
Inventory
Inventory represents the value of assets held by an organization for resale. Inventory can include goods available for sale (manufactured in-house or purchased from a third party), raw materials used to produce goods for sale, or a combination of both. Inventory value increases as goods are produced/purchased for sale and decreases as products are sold. The formula below outlines the general flow of inventory:
Beginning Balance + Purchases - Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) = Ending Inventory
Below are the most common methods used to value inventory:
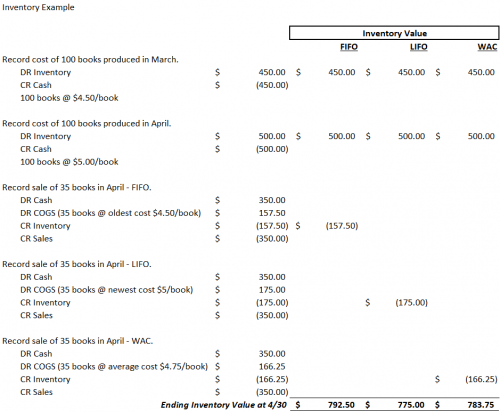
First-In-First-Out (FIFO): Assumes the oldest inventory purchases are the first to be sold and removed from the inventory balance. Cost of goods (COGS) is calculated using the cost of the earliest or oldest items purchased.
Last-In-First-Out (LIFO): Assumes the newest inventory purchases are the first to be sold and removed from the inventory balance. COGS is calculated using the cost of the newest or most recent items purchased.
Weighted Average Cost (WAC): COGS is calculated based on the average cost of all items purchased during a period.
Below is a comparison of the inventory value under the three methods based on the following scenario:
XYZ Organization produces books to sell to the general public. During March, the organization produced 100 books at a cost of $4.50 per book. Another 100 books were produced in April at a cost of $5 per book. During April, the organization also sold 35 books at $10 per book.